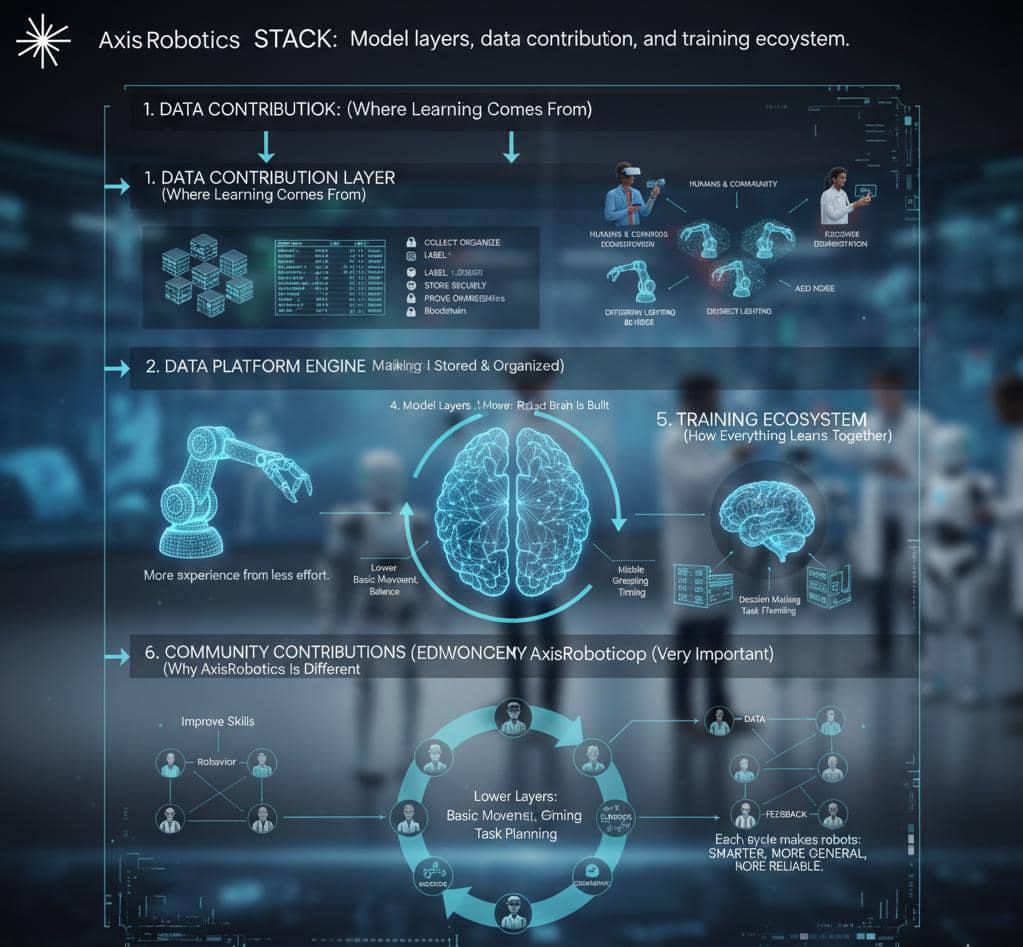
AI Learning Stack
Model layers, data contribution, and training ecosystem.
The AI Learning Stack is how AxisRobotics collects learning from many people, improves it with technology, and turns it into a smart robot brain.
Think of it as layers of learning, stacked on top of each other.
A stack means layers that work together.
In AxisRobotics, the AI Learning Stack answers three questions:
- Where does learning come from? (Data contribution)
- How is learning improved? (Augmentation)
- How does learning become intelligence? (Model training)
Humans & Community → Data Platform → Augmentation Engine → Model Layers → Shared Robot Intelligence
This is the starting point of intelligence. AxisRobotics believes robots should learn from many humans, not one company.
People contribute data by:
- Controlling robots in simulation
- Teleoperating robots remotely
- Demonstrating tasks
- Correcting robot mistakes
- Playing robot training tasks
Every contribution shows the robot how to move, what works, and what fails. Humans are the teachers.
Examples:
- Robot arm movements
- Joint positions
- Object positions
- Success or failure signals
- Timing and force
This data represents real experience, not theory.
The Data Platform is like a library for robot experience. It collects all contributed data, organizes it, labels it, stores it safely, and tracks who contributed what.
AxisRobotics uses blockchain here to:
- Prove data ownership
- Prevent cheating
- Reward contributors fairly
Data becomes a trusted asset, not just files.
Without a strong data platform:
- Data gets messy
- Learning becomes unreliable
- Contributors get ignored
AxisRobotics fixes this by making data verifiable, reusable, and valuable.
Augmentation means improving data without asking humans to do more work.
The Augmentation Engine:
- Takes existing data
- Creates variations
- Makes learning richer
Example:
- One robot movement becomes 100 slightly different movements
- Same task in different lighting
- Same action with different object sizes
More experience from less effort.
Real robots face different environments, noise, and unexpected situations.
Augmentation helps models learn:
- Flexibility
- Robustness
- Adaptability
It teaches robots: Don’t memorize — understand.
Model layers are levels of understanding inside the AI brain. Each layer learns something different.
Lower layers learn:
- Basic movement
- Motor control
- Balance
Middle layers learn:
- Skills (grasping, moving)
- Object interaction
- Timing
Higher layers learn:
- Decision making
- Task planning
- Choosing the right skill
Together, they form a general robot brain.
The training ecosystem is the full learning environment, not just one model.
It includes:
- Data contributors
- Simulation systems
- Training computers (GPUs)
- Model evaluators
- Feedback systems
Training happens continuously in cycles with community input. Learning never stops.
Most AI systems train in secret, use private data, and centralize intelligence.
AxisRobotics opens contribution to everyone, rewards useful data, and builds shared intelligence.
Community members improve robot skills, shape model behavior, and help discover better training methods.
The community is part of the brain.
Community contributes data → Data platform stores and verifies → Augmentation multiplies experience → Models learn patterns → Robots perform better → New data is generated → Community improves it again.
Each loop makes robots smarter, more general, and more reliable.
Think of a school:
- Students = AI models
- Teachers = Humans
- Textbooks = Data
- Practice = Simulation
- Exams = Real-world tests
- Graduation = Real robot skills
AxisRobotics is a global school where humans teach robots together.